Publication in Journal of Materials Chemistry A
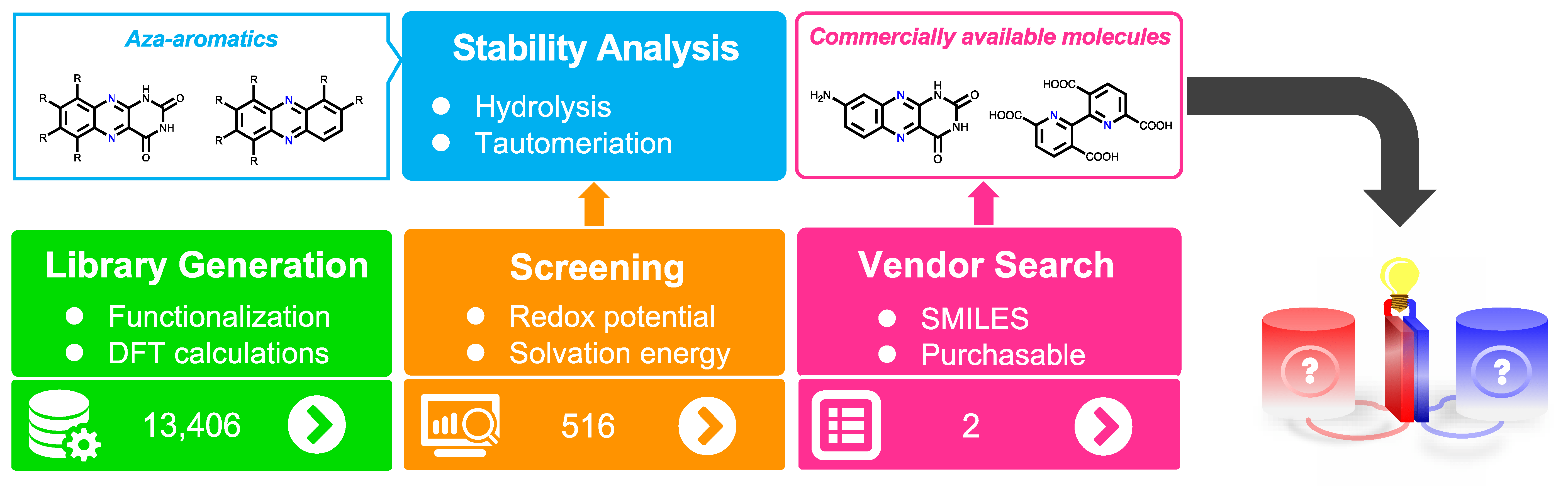
Using physics-based high-throughput screening that is coupled with machine learning and automated search of material purchasability, we discovered 516 new aza-aromatic compounds that can be used in redox flow batteries for efficient large-scale energy storage. Based on the new findings, we also proposed a molecular engineering strategy in a way to balance the inherent trade-offs among the redox, solubility and chemical stability features of the compounds, all together to improve the efficiency of energy storage. The study is published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A from The Royal Society of Chemistry.